CBD stands for cannabidiol, which is a naturally occurring compound found in the cannabis plant. It belongs to a class of compounds known as cannabinoids. CBD is one of the most well-known and studied cannabinoids, along with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). However, unlike THC, CBD is not psychoactive, meaning it does not produce a “high” or alter one’s state of mind.
CBD is extracted from hemp plants, which are a type of cannabis plant with low levels of THC. It can also be derived from marijuana plants, which have higher THC content, but CBD products derived from marijuana are subject to legal restrictions in many places.
CBD has gained popularity for its potential therapeutic benefits, especially in places like Florida, where questions about CBD Legal at Disney World Florida often arise. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating various physiological processes such as mood, pain sensation, immune function, and sleep.
Research suggests that CBD may have anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), and neuroprotective properties. It is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and insomnia.
CBD is available in various forms, including oils, tinctures, capsules, creams, and edibles. It is important to note that while CBD is generally considered safe, it can interact with certain medications, so it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before using CBD products, especially if you are taking other medications. Additionally, regulations regarding CBD vary by country and state, so it is essential to understand the legal status of CBD in your area before purchasing or using it.
What is CBD mean?
CBD, also known as cannabidiol, is a substance found in cannabis and hemp that does not cause intoxication. Products like CBD oils, gummies, and others are becoming increasingly popular as methods for alleviating symptoms such as anxiety, stress, and pain.

We usually link cannabis with getting high, but it’s possible to extract CBD from the plant to create products that don’t induce the high or require smoking. The chemical that produces the psychoactive effects of cannabis is called THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), but nowadays, cannabis-derived CBD products with little or no THC are available for symptom relief without a foggy mind.
Moreover, cannabis produces numerous cannabinoids, which are potentially therapeutic substances. As legalization spreads, we’re gradually discovering more about them, and so far, they appear to be quite beneficial for treating human illnesses.
Promos & Deals
What is the mechanism of action of CBD in the brain and body?
Our bodies have a group of receptors that interact with cannabinoids from cannabis, such as CBD. These receptors, which are present throughout the body, form the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex signaling system that regulates homeostasis in our bodies.
In other words, the endocannabinoid system maintains equilibrium by regulating communication between various bodily functions. Compounds like CBD interact with this system by imitating naturally occurring compounds known as endocannabinoids that the body produces.
CBD affects the activity of cannabinoid receptors in the human body, which stimulates the production of natural endocannabinoids. Additionally, CBD has an impact on activity beyond the endocannabinoid system, as it can interact with serotonin, dopamine, and opioid receptors.
The fact that CBD has the ability to interact with such a wide range of bodily systems suggests that it may have the potential to create new opportunities in the fields of medicine and psychiatry.
Does CBD produce a feeling of being high?
Unlike THC, CBD is not intoxicating. Why? Both THC and CBD are cannabinoids, but they behave very differently in our bodies. THC stimulates what are called CB1 receptors. When CB1 receptors are activated, humans generally experience feelings of euphoria—or, for some, anxiety and paranoia.
CBD doesn’t activate CB1 receptors, so we don’t feel euphoric, anxious, or stoned when taking it.
In fact, CBD can actually reduce THC’s ability to stimulate CB1 receptors, helping to block some of THC’s not-so-fun side effects. For those prone to anxiety and forgetfulness when consuming cannabis, CBD is a good tool to keep on-hand.
What are some illnesses that CBD has the potential to treat?
CBD is a multifaceted substance that has promising medical applications, which explains why it has recently become a popular “miracle cure” in the wellness industry.
However, given the lack of regulation on CBD oil and other products’ ingredients and the medical claims associated with them, it is reasonable to be skeptical. We actually encourage it.
Many of these claims are based on anecdotal evidence, preliminary research, and animal studies, but human studies are gradually filling in the gaps regarding CBD’s purported benefits. With this caveat in mind, here’s what we currently comprehend about the potential therapeutic uses of CBD.
Anxiety and CBD
If you ask around, it’s likely that you’ll find someone you know who swears by CBD as a way to relieve stress and anxiety. And, as of now, there’s no reason to doubt it; most studies on CBD suggest that it may help alleviate anxiety symptoms, potentially by influencing serotonin activity.
For immediate relief from acute stress and anxiety, it may be useful to vaporize strains high in CBD that contain a variety of botanical compounds, or to try a pure CBD oil that has been tested in a laboratory. While ingesting CBD oil can also help alleviate anxiety quickly, the effects are not instantaneous.
Pain and CBD
Based on current research, CBD has shown potential in alleviating two types of pain: neuropathic pain and inflammatory pain. However, it may not be as effective in treating other types of pain. THC, which causes euphoria, also has pain-relieving properties, so products containing both CBD and THC may be beneficial for pain management.
For individuals seeking pain relief, it may be helpful to start with a low dose of THC to determine if it enhances the pain-relieving effects of CBD without causing a noticeable high. In addition, cannabis has been shown to potentially replace or supplement opioid painkillers, and may even enhance the effectiveness of opioids, allowing patients to potentially reduce their dosage of pharmaceutical painkillers.

CBD’s Potential in Reducing Epileptic Seizures
Children with epilepsy often face a difficult choice between treatments that bring side effects that can drastically reduce their quality of life. However, CBD has shown promise as a treatment for seizures with relatively few side effects.
This has prompted researchers to study its potential further. In 2018, the FDA approved a CBD-based medicine called Epidiolex for treating two types of epilepsy. While early studies and anecdotal evidence have shown positive results, scientists have yet to determine why CBD may be effective in reducing seizures.
CBD and drug tests
While CBD is not typically screened for during a drug test, using CBD products can still result in a failed drug test due to the presence of THC. Most drug tests are designed to detect THC, and even hemp-derived full-spectrum CBD oils can contain up to 0.3% THC.
While this amount is not enough to cause intoxication, consuming large amounts of CBD oil could result in a positive test for THC.
Fortunately, there are options for those who wish to avoid THC. Broad-spectrum CBD oils and CBD isolates are two types of products that have had THC removed, while still retaining other beneficial compounds found in the hemp plant.
CBD Legal situation
Cannabis has been federally illegal since 1937, including hemp until the Agricultural Improvement Act of 2018. This law, also known as the farm bill, removed hemp and its derivatives from the Controlled Substances Act.
Although both hemp and high-resin cannabis produce CBD, they are legally defined differently. Legally, hemp and its products must contain less than 0.3% THC.
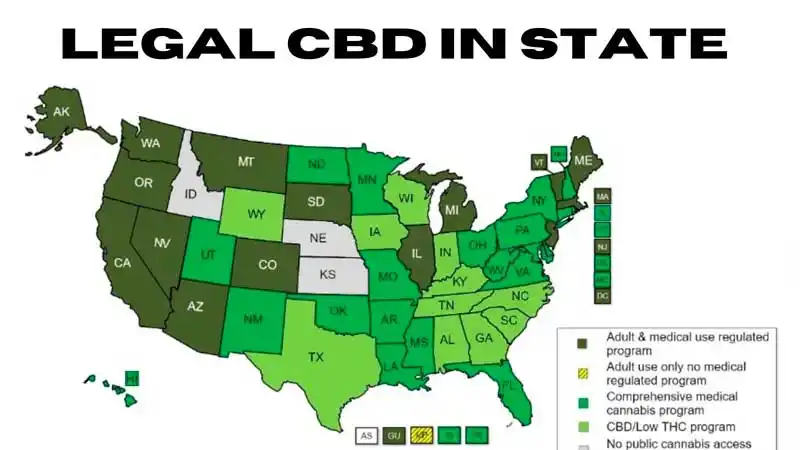
However, the legality of CBD derived from hemp can still vary by state in the US. CBD in all forms is still prohibited in Idaho, Iowa, and South Dakota, while in other states such as Alaska, California, and Washington, only licensed cannabis shops can sell CBD in food or beverage forms.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is currently developing regulatory guidelines for CBD products, with the first draft expected to arrive in early 2020. Until then, adding CBD to food or labeling it as a dietary supplement is illegal according to the FDA.
How does CBD derived from hemp differ from that derived from cannabis?
CBD can be derived from both hemp and cannabis plants, and while the molecule itself remains the same, there are significant distinctions between CBD products sourced from each plant.
When discussing hemp, we are referring to the industrial crop with low resin content that is typically used to manufacture clothing, textiles, food, and other goods. In contrast, we use the term cannabis to refer to the high-resin plants cultivated for medical or recreational purposes. So which source is superior?
Let’s take a quick look at the advantages and disadvantages of each.
CBD derived from hemp:
Advantage. Hemp is legal at the federal level in the US (although it is important to verify that it is legal in your state), and CBD products derived from hemp are easily accessible for purchase online and in retail stores. Hemp generates negligible amounts of THC, making it an attractive option for individuals who want to avoid THC entirely.
Disadvantages. Compared to high-resin cannabis, hemp generates a restricted range of therapeutic compounds. Hemp products currently lack regulation, which can result in unchecked potencies, questionable ingredients, and dubious claims.
CBD derived from cannabis
Advantages of Cannabis-derived CBD include a wider range of therapeutic compounds available in larger quantities compared to hemp. Additionally, these products undergo strict regulation and testing in accordance with state laws. However, a significant disadvantage is that cannabis-derived CBD is only accessible in states where cannabis is legal, making it inaccessible to consumers in states where it is not legal.
CBD Very Cherry Berry
The CBD Very Cherry Berry is a hybrid between Cherry Wine and Berry, renowned for its high CBD content (16%-18%) and low THC content (0.3%-0.5%). This genetics boasts a highly aromatic terpene profile with sweet berry and ripe cherry notes.
This strain offers medicinal benefits such as pain relief, inflammation reduction, and anxiety reduction. It may also be useful for treating sleep disorders and stimulating appetite.
The flowering time for CBD Very Cherry Berry is around 8-9 week (flowering) and can be harvested in late September outdoors. Indoors, it can produce about 1.31-1.64 oz/ft2, while outdoors it can yield up to 15-19 oz/plant.
As CBD Very Cherry Berry is mostly sativa genetics, you can use indoor growing techniques such as SCROG since with a mesh, you can spread out its arms and with that get more uniform arms with colas that are going to be full of buds.
Outdoors you can take advantage of the end of autumn to sow the seeds indoors and then, in spring when the plant is strong, it can be taken outdoors and transplanted into a larger pot. With this technique you make sure that the roots grow big and strong and in the end you will get a great harvest.
Remember to use mycorrhiza from the beginning of the crop when you sow the seed, to stimulate microbiotic life and the growth of a very powerful root system.

CBD CA-1 (1:20)
CBD CA-1 (1:20) is a sativa cannabis strain with a THC:CBD ratio of 1:20, which means it has very low levels of THC and high levels of CBD (18%-20%). This strain is a good option for those seeking the benefits of CBD without experiencing the psychoactive effects of THC.
Regarding indoor harvests, CBD CA-1 (1:20) typically has a medium yield of 1.31 oz/ft2 and requires 8 to 9 weeks of flowering. On the other hand, in outdoor cultivation, this strain will be ready to be harvested in late September or early October, with a similarly medium yield of 14 oz/plant.
In terms of flavor and aroma, CBD CA-1 (1:20) has an earthy, fresh lemon, and sweet taste with notes of lemon and pine. The terpenes present in CBD CA-1 (1:20) include pinene, limonene, and linalool.
CBD CA-1 (1:20) has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including chronic pain, inflammation, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, this strain may be useful in treating neurological disorders such as epilepsy and Tourette’s syndrome.
If you grow CBD CA-1 (1:20) outdoors, you can achieve maximum yields by raising these plants in large pots of 50 liters or more and starting the cultivation in small pots to effectively promote root growth. Indoors, you can apply techniques like LST to stretch out its branches and also SCROG to obtain uniform and highly productive plants.
CBD Mango 1:1
Mango CBD 1:1 is a cannabis strain known for its balanced levels of CBD and THC. It has a unique flavor and aroma profile that is defined by its dominant terpenes, including myrcene, limonene, and beta-caryophyllene.
This strain has a sweet and tropical taste, with notes of mango, pineapple, sweet and tropical. In terms of CBD and THC levels, Mango CBD 1:1 typically contains around 8-10% of CBD and 6%-8% THC. This makes it a great choice for those who want to experience the benefits of CBD without the psychoactive effects of THC.
When grown outdoors, Mango CBD 1:1 can yield up to 7 oz/plant, while indoor growers can expect a yield of around 1.64-1.97 oz/ft2. The flowering time for this strain is around 9-11 weeks when grown indoors, and it can be harvested in late September to early October when grown outdoors.
The effects of Mango CBD 1:1 are known to be relaxing and uplifting, with a mild cerebral buzz that can help alleviate anxiety and stress. It’s also been reported to help with pain, inflammation, and nausea.
If you’re growing CBD Mango 1:1 in areas with a short summer, humid climates, or places where sudden rainfall can occur without warning, you should closely monitor the plant and check its flowers daily to prevent the onset of fungus that can damage the harvest. It’s important to use some form of fertilizer or protector to prevent the appearance of fungi and other diseases. We recommend providing vitamins to help enhance the immune system of your CBD Mango 1:1 plants.
















